Imagine a world where doctors don’t just rely on stethoscopes and charts but can actually see inside your body without any invasive procedures. Sounds like science fiction, right? Well, welcome to the future! Augmented reality in healthcare is transforming the way medical professionals diagnose and treat patients, making procedures more precise and less daunting.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) significantly enhances various healthcare practices, allowing professionals to merge digital information with real-world scenarios. Surgeons utilize AR to overlay critical anatomical information on a patient’s body during procedures, improving precision and minimizing risks. Medical students benefit from AR by practicing complex procedures in a safe, simulated environment, which boosts their confidence and skills.
In diagnostics, AR plays a pivotal role in visualizing internal organs and tissues non-invasively. Physicians can view 3D models generated from imaging data, enabling quicker and more accurate assessments. This technology lessens the reliance on traditional imaging techniques, reducing inconveniences for patients.
Patient education sees improvement through AR applications. Engaging visual content helps patients understand their conditions better, making treatment plans more comprehensible. Furthermore, AR aids in developing tailored rehabilitation programs by providing real-time feedback on a patient’s performance during therapy sessions.
A variety of AR devices and applications exist, catering to diverse needs within the medical field. Designers tailor solutions ranging from wearable headsets to smartphone applications, each intended to enhance a specific aspect of healthcare delivery. Integration of AR into electronic health records (EHR) is also gaining traction, facilitating seamless access to relevant patient data.
Research indicates that AR can lead to increased efficiency and improved outcomes in healthcare settings. Data shows that AR usage in surgery reduces the time spent in operating rooms by up to 30%. Hospitals adopting AR technology report higher satisfaction rates from both medical staff and patients, indicating its effectiveness in modern healthcare.
Benefits of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
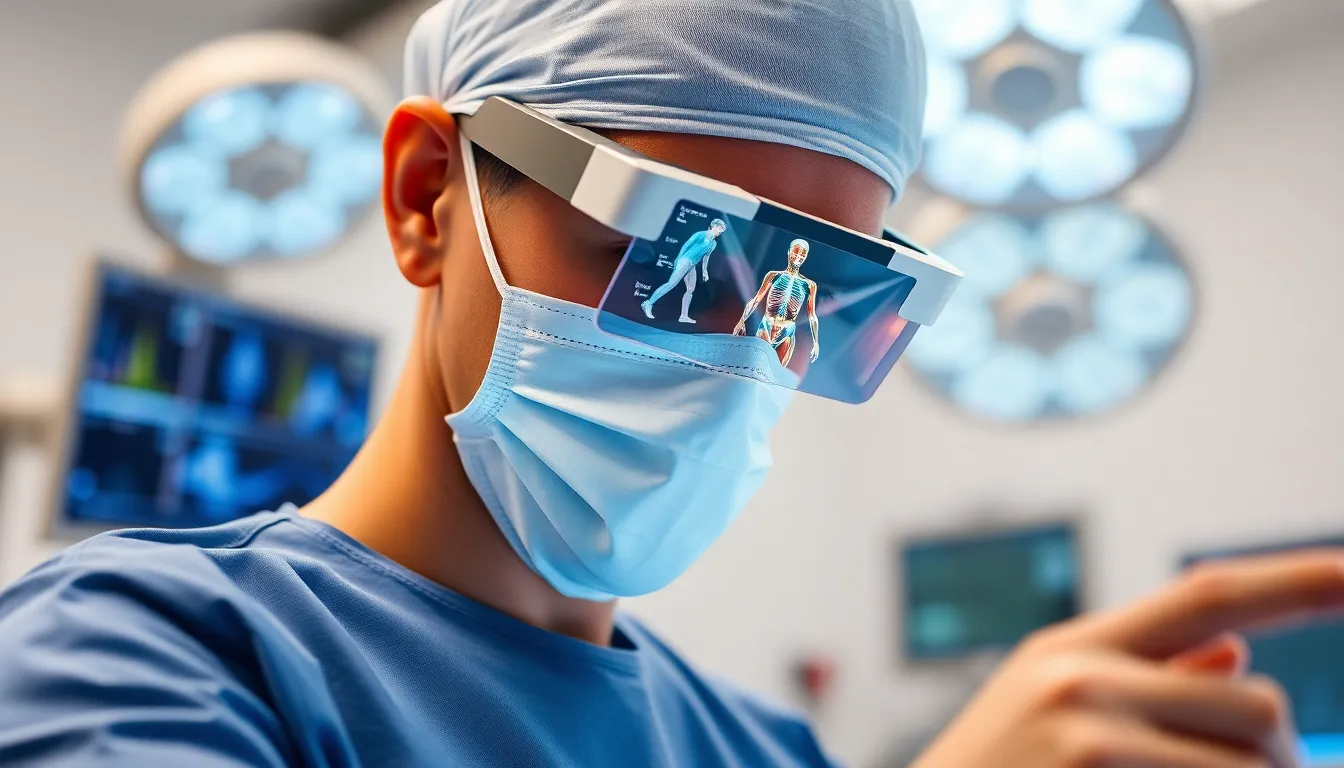
Augmented reality (AR) offers significant advantages in healthcare, transforming traditional practices and enhancing patient experiences.
Improved Surgical Precision
AR technology elevates surgical procedures by providing real-time visualizations of patient anatomy. Surgeons access critical data, such as 3D overlays of organs, directly within their field of view. This integration leads to greater accuracy during operations, reducing the likelihood of errors. Research indicates that AR can decrease operating room time by up to 30%, showcasing its efficiency. Enhanced visualization allows for better decision-making, ultimately leading to safer surgical outcomes for patients. Surgeons gain the confidence needed to tackle complex cases, contributing to overall improved patient care.
Enhanced Patient Education
Patient understanding of medical conditions improves significantly with AR’s interactive technology. Engaging visual content, such as 3D models, helps patients comprehend their diagnoses and treatment plans more effectively. AR fosters a more informative dialogue between healthcare providers and patients, creating a collaborative environment. Patients often feel more in control of their health when they visualize their conditions. This clarity leads to higher satisfaction rates among patients, as they actively participate in their healthcare decisions. Educational applications using AR not only demystify procedures but also empower patients to ask informed questions.
Applications of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) plays a pivotal role in enhancing healthcare by improving training, diagnostics, and surgical processes. Its diverse applications provide valuable support to medical professionals and patients alike.
Medical Training and Simulation
Medical training benefits significantly from AR technology. The ability to engage in realistic simulations allows students to practice complex procedures without real-life consequences. Additionally, AR enhances understanding of anatomical structures through interactive 3D models. These visual aids help students retain critical information more effectively. Institutions that incorporate AR in their curricula experience improved learning outcomes and increased student confidence. Moreover, students gain hands-on experience that translates to better performance in clinical settings.
Patient Diagnostics
Patient diagnostics undergo a transformation with AR integration. By visualizing internal organs and tissues through 3D representations, physicians can make quicker and more accurate assessments. This non-invasive approach reduces the need for multiple tests, making the diagnostic process more efficient. Enhanced visualization tools also assist in identifying abnormalities that may not be immediately apparent with traditional imaging techniques. As a result, patients benefit from a higher standard of care and reduced anxiety associated with diagnostic procedures.
Surgical Assistance
Surgical assistance greatly improves thanks to AR technology. Surgeons can overlay critical anatomical information directly onto their field of vision during procedures. This real-time information allows for improved precision in targeting specific areas, which minimizes risks during operations. Studies show that AR can decrease operating room time by up to 30%, enhancing overall surgical efficiency. With the integration of 3D models and live data, surgical teams achieve better outcomes and increased patient safety. Thus, AR has become an invaluable asset in modern surgical practices.
Challenges and Limitations
Augmented reality in healthcare presents notable challenges and limitations that require attention. Technological barriers hinder broader implementation and effectiveness.
Technological Barriers
Innovation in AR technology still faces hurdles. Limited bandwidth can disrupt data transmission, affecting real-time overlays during procedures. Many healthcare facilities lack the necessary infrastructure to support AR applications efficiently. Additionally, high costs associated with advanced AR devices hinder widespread adoption among smaller practices. Compatibility with existing systems shows variance, creating integration issues that complicate usage. Ensuring user-friendly interfaces remains a challenge, as medical staff may experience difficulties in adapting to complex AR systems.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical concerns arise when implementing AR in healthcare settings. Patient privacy becomes a crucial issue, as AR applications often require sensitive personal data. Securing this information against breaches is vital. Additionally, relying too heavily on AR could lead to decreased hands-on experience for medical trainees. Concerns about informed consent exist when patients interact with AR content, highlighting the importance of transparency. Balancing innovation with ethical guidelines presents ongoing challenges for health professionals, ensuring responsible use of technology.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Innovations in augmented reality (AR) are set to transform healthcare further in the coming years. Enhanced training tools will enable medical students and professionals to practice using AR simulations that replicate real-life scenarios. This hands-on experience fosters skill development while minimizing patient risk.
Adoption of AR for telemedicine is gaining traction. Remote consultations enhanced by AR technology allow healthcare providers to interact with patients visually, improving diagnostic accuracy. Patients engage more effectively as they can visualize treatment processes and understand procedures better.
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with AR presents new possibilities. AI algorithms can analyze patient data alongside AR visualizations, providing personalized treatment suggestions. This combination will make decision-making more efficient and informed.
Data security remains a priority as AR applications evolve. Patient privacy concerns will drive the development of more secure AR systems, ensuring compliance with regulations. Providers must focus on implementing robust data protection measures to maintain trust.
Collaboration among healthcare professionals is expected to increase with AR tools. Multi-disciplinary teams will utilize AR to share patient information and treatment plans effectively. This communal approach enhances patient care by fostering a comprehensive understanding of individual cases.
Emerging AR devices will likely become lighter and more user-friendly. Wearable AR systems can project visual information directly into a surgeon’s field of view, streamlining processes. Such advancements promise to reduce operating room time further, contributing to safer surgical outcomes.
For patient education, engaging AR content will evolve. Visual aids will become more sophisticated, making complex medical concepts easier to grasp. As patients become more informed, their involvement in healthcare decisions will grow, leading to improved outcomes.
Overall, future trends in AR indicate a path toward more efficient, accurate healthcare solutions while maintaining a strong emphasis on ethical practices and patient privacy.
The integration of augmented reality in healthcare is reshaping how medical professionals approach diagnostics and treatments. This technology not only enhances precision but also fosters a more engaging patient experience. As AR continues to evolve it promises to streamline surgical processes and improve training for medical students.
While challenges like technological barriers and ethical considerations remain, the potential benefits of AR far outweigh these obstacles. Future developments will likely lead to more user-friendly applications that prioritize patient privacy and enhance collaboration among healthcare providers. Embracing AR in healthcare could ultimately result in safer and more effective patient care.


